Understanding Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
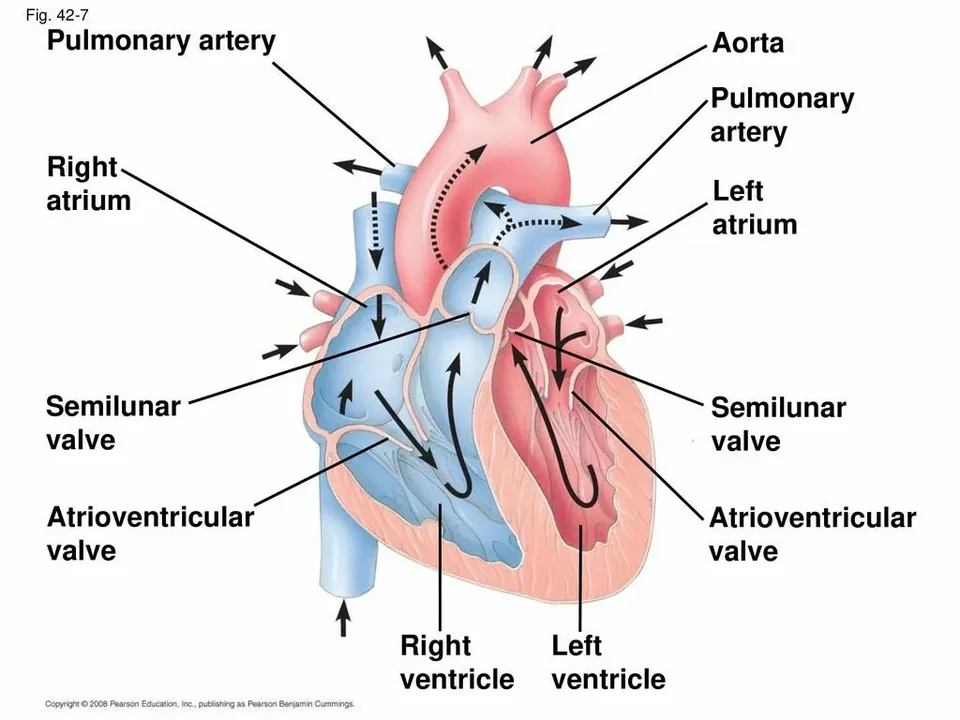
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare but serious condition that affects the blood vessels in the lungs. It causes the walls of the pulmonary arteries to become thick and stiff, making it harder for blood to flow through them. This increased pressure can eventually lead to heart failure and other complications. As a patient living with PAH, it's crucial to take care of yourself physically, mentally, and emotionally. In this article, we'll explore the importance of self-care for PAH patients and provide some tips to help you maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Managing Stress and Anxiety
Living with a chronic illness like PAH can be stressful and anxiety-inducing. This stress can negatively impact your overall health and well-being, making it even more important to find ways to manage these emotions. Some effective stress management techniques include practicing mindfulness, engaging in deep breathing exercises, and participating in calming activities such as yoga or meditation.
It's also important to maintain a support system of friends, family, and healthcare professionals who can help you navigate the challenges of living with PAH. Communicate openly with your loved ones about your feelings and concerns, and consider joining a support group specifically for individuals with PAH or other chronic illnesses to connect with others who understand what you're going through.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet
Eating a well-balanced diet is essential for maintaining overall health, and it's especially important for PAH patients. Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods can help provide your body with the energy and nutrients it needs to function properly. Focus on incorporating whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your meals.
It's also important to limit your salt intake, as excessive sodium can cause fluid retention and exacerbate PAH symptoms. Be mindful of processed foods, which often contain high levels of sodium, and try cooking at home using fresh ingredients whenever possible. Don't forget to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day, as this can help maintain proper blood flow and prevent dehydration.
Staying Physically Active
While it's important to listen to your body and not overexert yourself, engaging in regular physical activity can help improve your overall well-being and support your body's ability to manage PAH symptoms. Exercise can help strengthen your heart and lungs, improve circulation, and reduce stress and anxiety.
Discuss your exercise plan with your healthcare team, as they can help you determine the appropriate level of activity for your specific needs. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are often recommended for PAH patients. Always start slow and gradually increase the intensity of your workouts as your body becomes more accustomed to the activity. Remember to listen to your body and stop exercising if you feel lightheaded, dizzy, or short of breath.
Monitoring Your Symptoms and Medication
Regularly monitoring your symptoms and taking your medication as prescribed is a critical part of managing PAH. Keep track of any changes in your symptoms, such as increased shortness of breath, fatigue, or chest pain, and report these changes to your healthcare team promptly. They can help determine if any adjustments need to be made to your treatment plan.
It's also important to take your medication exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. This may include taking multiple medications at various times throughout the day. Set reminders for yourself to ensure you don't miss any doses, and keep a medication log to track when you've taken each dose. By staying vigilant about your symptoms and medication, you can help maintain your health and prevent potential complications from PAH.
Getting Adequate Rest and Sleep
Ensuring you get enough rest and sleep is essential for maintaining your overall health and well-being as a PAH patient. Adequate sleep can help reduce stress, improve your mood, and support your body's natural healing processes. Aim for at least 7-9 hours of sleep each night, and establish a consistent sleep schedule to help regulate your body's internal clock.
Create a relaxing bedtime routine to help signal to your body that it's time to wind down for the night. This might include activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or engaging in gentle stretches or meditation. Limit your exposure to screens and electronics before bed, as the blue light emitted by these devices can interfere with your body's production of melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep. By prioritizing rest and sleep, you can help support your body's ability to manage PAH and maintain overall health.

Write a comment