Acetazolamide – Uses, Side Effects, and Dosage Guide
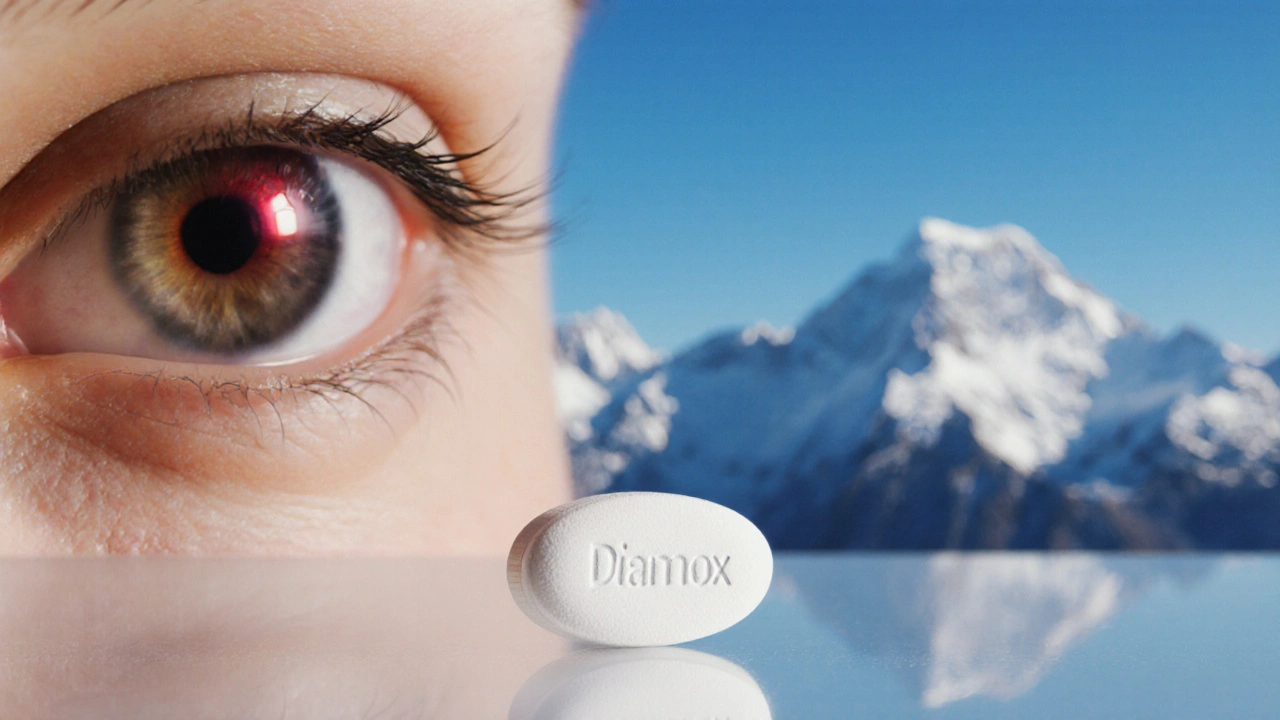
When working with Acetazolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that reduces fluid buildup in the eye and lowers seizure activity. Also known as Diamox, it is prescribed for several conditions that involve excess fluid or pressure. For example, Glaucoma, an eye disease where pressure damages the optic nerve often responds quickly to Acetazolamide because the drug lowers intra‑ocular pressure by limiting aqueous humor production. This connection makes Acetazolamide a first‑line oral option when eye‑drops alone aren’t enough. Understanding how the drug works helps you see why doctors pair it with other pressure‑lowering agents and why regular eye‑pressure checks are essential during treatment.
Beyond the Eye: Other Key Applications
Acetazolamide isn’t just for eye health. It’s also the go‑to medication for Altitude Sickness, a condition caused by rapid ascent to high elevations leading to headache, nausea and breathlessness. By promoting a mild metabolic acidosis, the drug stimulates breathing, delivering more oxygen to tissues. The same acid‑base shift can be useful in controlling certain seizure disorders, such as Epilepsy, a neurological disease characterized by recurrent seizures. Here, Acetazolamide’s ability to alter cerebrospinal fluid composition helps reduce neuronal excitability. These diverse actions show how a single chemical class—carbonic anhydrase inhibitors—can impact both ophthalmology and neurology, linking pressure regulation, breathing control, and seizure reduction under one pharmacologic roof.
When you start Acetazolamide, dosing usually begins at 250 mg once or twice daily, adjusted based on the condition being treated and your kidney function. Because the drug pushes bicarbonate out of the body, you might notice increased urination, a tingling sensation in your hands or feet, or a slight metallic taste. More serious but rare effects include severe metabolic acidosis, kidney stones, or allergic skin reactions. Monitoring blood electrolytes and staying well‑hydrated can keep these risks low. If you experience persistent fatigue, confusion, or a rapid heartbeat, contact your provider right away. Armed with this practical guidance, you’ll be ready to evaluate the articles below, which dive deeper into dosing nuances, drug interactions, and real‑world patient experiences with Acetazolamide.
- By Percival Harrington
- /
- 7 Oct 2025
Diamox (Acetazolamide) vs Alternatives: In‑Depth Comparison
A clear, side‑by‑side comparison of Diamox (acetazolamide) with common alternatives, covering uses, dosing, side effects, and how to pick the right drug.