Statins and Insulin Sensitivity: What You Need to Know
When you take a statin, a class of drugs used to lower LDL cholesterol by blocking an enzyme in the liver. Also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, they’re among the most prescribed medications worldwide for heart disease prevention. But behind their benefits lies a quieter, less talked-about effect: how they influence your body’s insulin sensitivity, how well your cells respond to insulin to pull glucose out of the bloodstream. It’s not a myth—some people on statins see their blood sugar rise slightly. That doesn’t mean everyone will, but it’s something worth understanding if you’re managing diabetes, prediabetes, or just trying to stay healthy.
Statins like rosuvastatin, a potent statin known for strong LDL-lowering effects and atorvastatin are especially linked to small increases in fasting blood sugar. Studies show about a 10-12% higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes over several years in people already at risk—like those who are overweight, have high triglycerides, or have a family history of diabetes. The effect is small, but real. For most, the heart protection from lowering LDL far outweighs this risk. But if your blood sugar is already creeping up, your doctor should track it closely. It’s not about stopping statins—it’s about adjusting your plan. Maybe you need more movement, better sleep, or a change in diet. Some people even benefit from adding metformin, not because they have diabetes yet, but because it helps counteract the subtle insulin resistance statins can trigger.
This isn’t just about pills. It’s about how your body works as a system. insulin resistance, a condition where cells don’t respond properly to insulin, leading to higher blood sugar often shows up before diabetes. And statins, while helping your arteries, can sometimes nudge your metabolism in the wrong direction. That’s why monitoring isn’t optional—it’s part of smart care. If you’re on a statin and you’ve noticed more fatigue, increased thirst, or unexplained weight gain, don’t ignore it. Talk to your provider. Get your HbA1c checked. Look at your fasting glucose. These aren’t scary numbers—they’re signals.
The posts below cover real-world cases and science-backed insights. You’ll find how rosuvastatin affects blood sugar in practice, what alternatives exist for people worried about metabolic side effects, and how lifestyle changes can offset risks. You’ll also see how GLP-1s, once seen only as weight-loss drugs, are now being used to protect insulin sensitivity in people taking statins. And you’ll learn how to spot early signs of trouble before it becomes a bigger problem. This isn’t theory. It’s what people are experiencing—and what doctors are starting to act on.
- By Percival Harrington
- /
- 26 Nov 2025
Pitavastatin and Diabetes Risk: What You Need to Know About Metabolic Effects
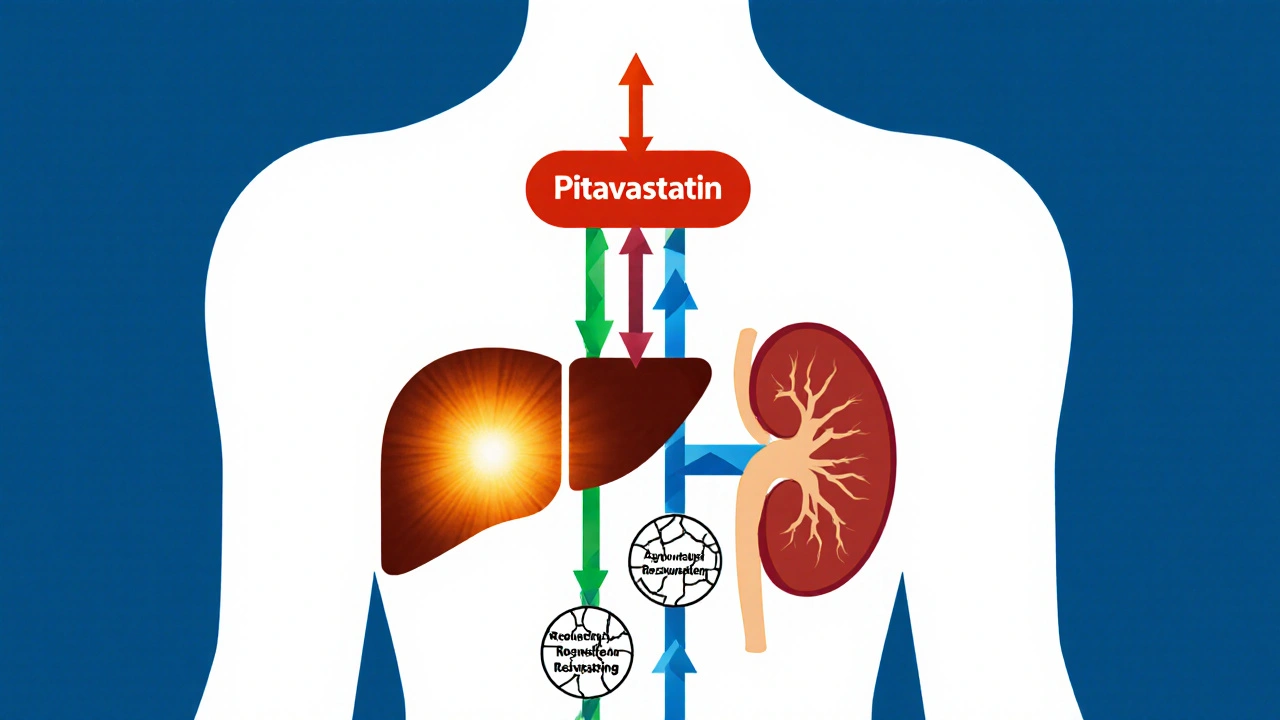
Pitavastatin offers a safer metabolic profile than other statins, with lower risk of raising blood sugar and triggering diabetes. Ideal for prediabetic patients needing cholesterol control without worsening insulin resistance.