Collagen: What It Is, Why You Need It, and How to Use It
If you’ve seen ads promising smoother skin or stronger joints, they’re probably talking about collagen. In plain terms, collagen is a protein that makes up most of the connective tissue in your body – think skin, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
Types of Collagen You’ll Meet
There are at least 28 different kinds, but three dominate supplements:
- Type I: found in skin, bone, and tendons. It’s the go‑to for beauty‑focused products.
- Type II: mostly in cartilage. If you’re looking after joint comfort, this is the one to watch.
- Type III: works alongside Type I in skin and blood vessels, helping with elasticity.
Knowing which type matches your goal makes buying easier and saves money.
How Collagen Works for Your Body
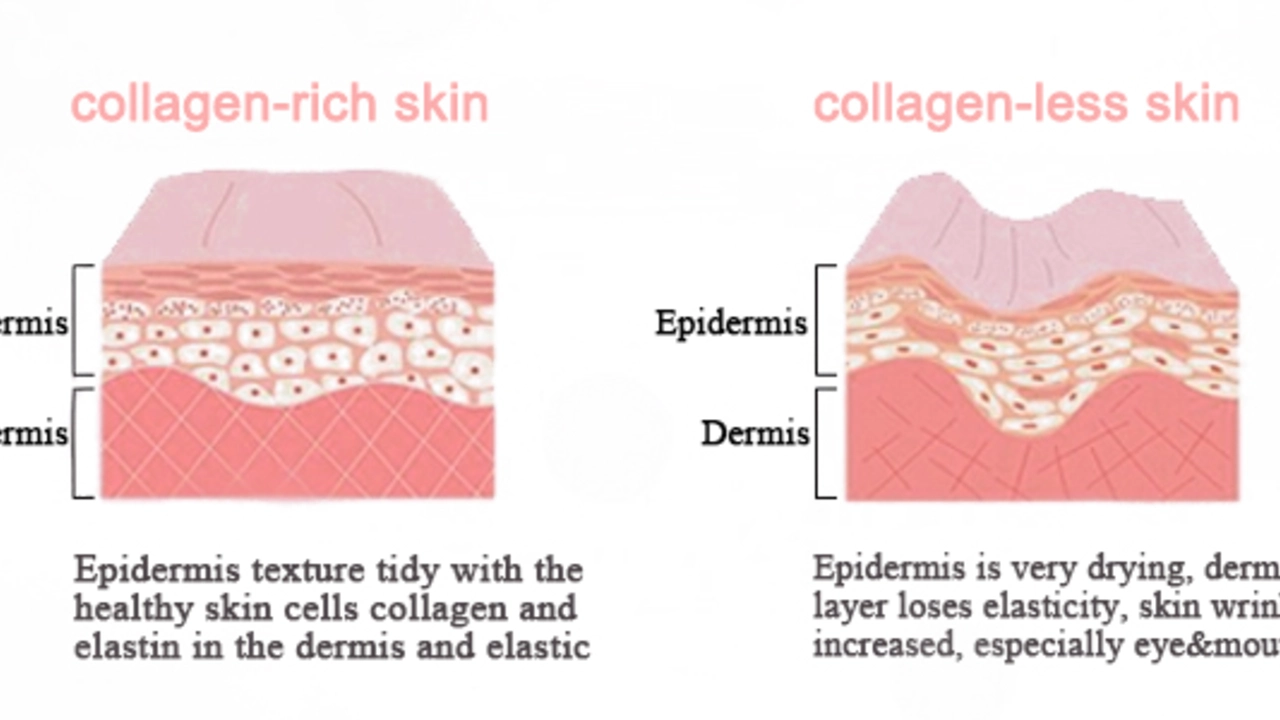
When you eat collagen, your stomach breaks it down into amino acids. Those building blocks get reshuffled into the proteins your body needs. That’s why a steady supply can support skin firmness, hair strength, and joint cushioning.
Research shows daily doses of 5‑10 grams can improve skin hydration and reduce wrinkle depth after a few weeks. For joint health, studies suggest 10 grams of Type II hydrolyzed collagen may ease stiffness in people with osteoarthritis.
Choosing the Right Collagen Supplement
Here are three quick checks before you click ‘add to cart’:
- Source: Bovine (cow) gives mostly Type I & III, marine (fish) offers highly bioavailable Type I, and chicken provides Type II.
- Form: Powders mix into drinks, capsules are convenient, and gummies taste like candy but may contain extra sugars.
- Purity: Look for products tested for heavy metals and free from added hormones or antibiotics.
If you’re vegetarian or vegan, plant‑based “collagen boosters” with vitamin C, silica, and amino acids can help your body make its own collagen.
How to Take Collagen for Best Results
Take it on an empty stomach or with a small amount of protein – the exact timing isn’t critical, but consistency is. Mixing powder into coffee, smoothies, or even oatmeal works well and hides any mild flavor.
A typical regimen looks like this:
- Morning: 5 g collagen powder in your coffee or smoothie.
- Evening: If you prefer capsules, pop them with dinner.
Pair collagen with vitamin C‑rich foods (citrus, berries) because vitamin C helps convert amino acids into new collagen fibers.
Potential Side Effects and Who Should Skip It
Collagen is generally safe. A few people report mild stomach upset or a lingering aftertaste. If you have allergies to fish or beef, choose the source accordingly.
Pregnant or nursing folks should check with a doctor before starting any supplement, just to be sure it fits their health plan.
Bottom Line
Collagen can be a handy addition if you’re after healthier skin, stronger joints, or better overall tissue support. Pick the right type for your goal, verify purity, and stick to a daily routine. Pair it with vitamin C, stay consistent, and you’ll likely notice small but real improvements within weeks.
- By Percival Harrington
- /
- 21 Jul 2023
The role of collagen in managing skin irritations.
In my recent research, I've discovered how vital collagen is in managing skin irritations. This protein, naturally produced by our bodies, plays a crucial role in the healing process of the skin by promoting regeneration and reducing inflammation. When skin irritations occur, a boost of collagen can help to soothe and repair the skin effectively. Additionally, collagen aids in maintaining skin elasticity and hydration, further preventing potential irritations. In short, collagen is a key player in maintaining healthy skin and managing irritations.