Antibiotic Risk: What You Need to Know About Side Effects, Resistance, and Safe Use
When you take an antibiotic, a medication designed to kill or slow the growth of bacteria. Also known as antibacterial agents, they save lives—but only when used correctly. Misuse turns them into a silent threat, fueling antibiotic resistance, the process where bacteria evolve to survive drug exposure and making common infections harder to treat.
Every time you take an antibiotic unnecessarily—like for a cold or flu—you’re not helping yourself. You’re training bacteria to fight back. The side effects antibiotics, ranging from mild stomach upset to life-threatening diarrhea caused by C. diff, are just the tip of the iceberg. Over time, resistant strains spread in hospitals, homes, and even food. The CDC says at least 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections happen in the U.S. every year, and more than 35,000 people die from them. That’s not a future scare—it’s happening now.
Some people think if a little is good, more is better. That’s not true. Taking leftover pills, skipping doses, or using antibiotics prescribed for someone else increases your antibiotic risk, the chance you’ll develop a resistant infection or suffer serious side effects. It also makes future treatments less effective—for you and everyone around you. Even your doctor can’t always tell if an infection is bacterial or viral. That’s why asking questions matters. Did you get tested? Is this really needed? Are there safer options?
What you’ll find here are real stories, clear facts, and practical advice from posts that dig into how antibiotics affect your body, how resistance spreads, and what you can do to protect yourself. From monitoring side effects to understanding why some doctors hesitate to prescribe, these articles give you the tools to make smarter choices. You won’t find fluff. Just what you need to know before the next prescription is written.
- By Percival Harrington
- /
- 4 Dec 2025
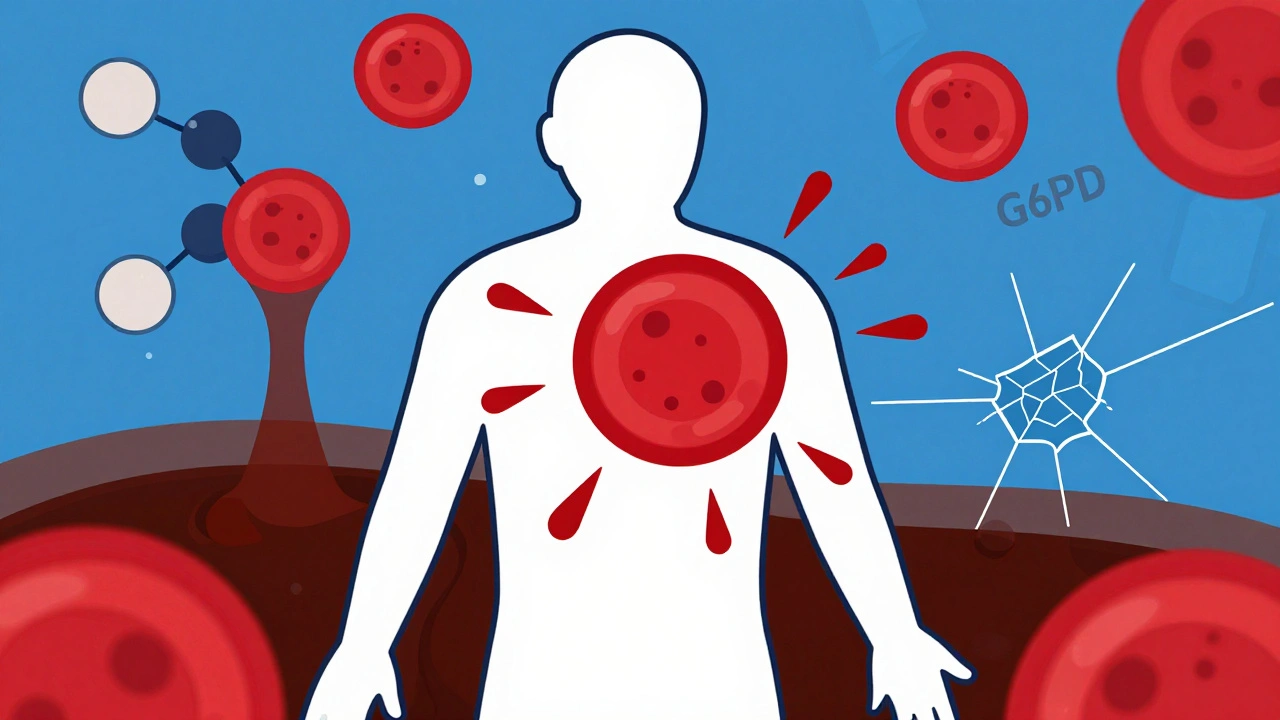
Nitrofurantoin and Hemolytic Anemia: What You Need to Know About G6PD Deficiency Risk
Nitrofurantoin can cause life-threatening hemolytic anemia in people with G6PD deficiency. Learn who’s at risk, what symptoms to watch for, and safer alternatives for treating UTIs.