Hormone Therapy Explained: Benefits, Risks, and Real‑World Use
When talking about hormone therapy, the medical use of hormones to treat deficiencies, manage conditions, or improve quality of life. Also known as HT, it covers everything from estrogen supplements for women to thyroid hormone pills for hypothyroidism. Hormone therapy bridges the gap between natural hormone levels and the body’s needs, often after surgery, during aging, or when a disease disrupts production.
One of the most common branches is hormone replacement therapy, a specific type of hormone therapy that replaces estrogen, progesterone, or testosterone lost during menopause or other hormonal shifts. Many people think HRT is only about relieving hot flashes, but it also helps protect bone density, improve mood, and support cardiovascular health when used correctly. HRT requires regular blood tests and dose adjustments, because too much or too little can swing the balance the wrong way.
How Menopause, Thyroid Issues, and Blood Clot Risks Connect to Hormone Therapy
menopause, the natural decline of reproductive hormones in women typically occurring between ages 45‑55 often triggers the first conversation about hormone therapy. Women experiencing night sweats, mood swings, or bone loss may turn to estrogen‑based HT to smooth the transition. At the same time, hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid that releases excess thyroid hormones can be managed with anti‑thyroid drugs, but some patients need controlled hormone therapy to bring levels back into balance after treatment.
The link between hormone therapy and deep vein thrombosis, a blood clot that forms in the deep veins, usually in the legs, and can travel to the lungs is a key safety concern. Estrogen‑based HT can increase clotting factors, so clinicians assess personal clot history, smoking status, and lifestyle before prescribing. The semantic triple here: hormone therapy requires careful monitoring of clot risk, and deep vein thrombosis influences the decision to start or stop therapy.
Beyond women’s health, hormone therapy also plays a role in men’s testosterone replacement, adrenal insufficiency, and even gender‑affirming care. Each scenario brings its own set of monitoring parameters—blood pressure, lipid profiles, and liver function tests—to keep the therapy safe and effective. The overall picture is that hormone therapy encompasses a wide range of applications, each needing a tailored approach.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive into specific drugs, safety tips, and real‑world comparisons—from lenalidomide’s off‑label use in lupus to practical guides on buying generic meds online. Whether you’re weighing the pros of HRT, checking clot risk, or simply curious about how thyroid hormones are regulated, the collection offers actionable insights you can apply right now.
- By Percival Harrington
- /
- 22 Oct 2025
Tibolone and Migraines: Risks, Triggers, and Management Tips
Learn how tibolone can trigger migraines, who’s at risk, and practical ways to manage headaches while treating menopausal symptoms.
- By Percival Harrington
- /
- 1 Oct 2025
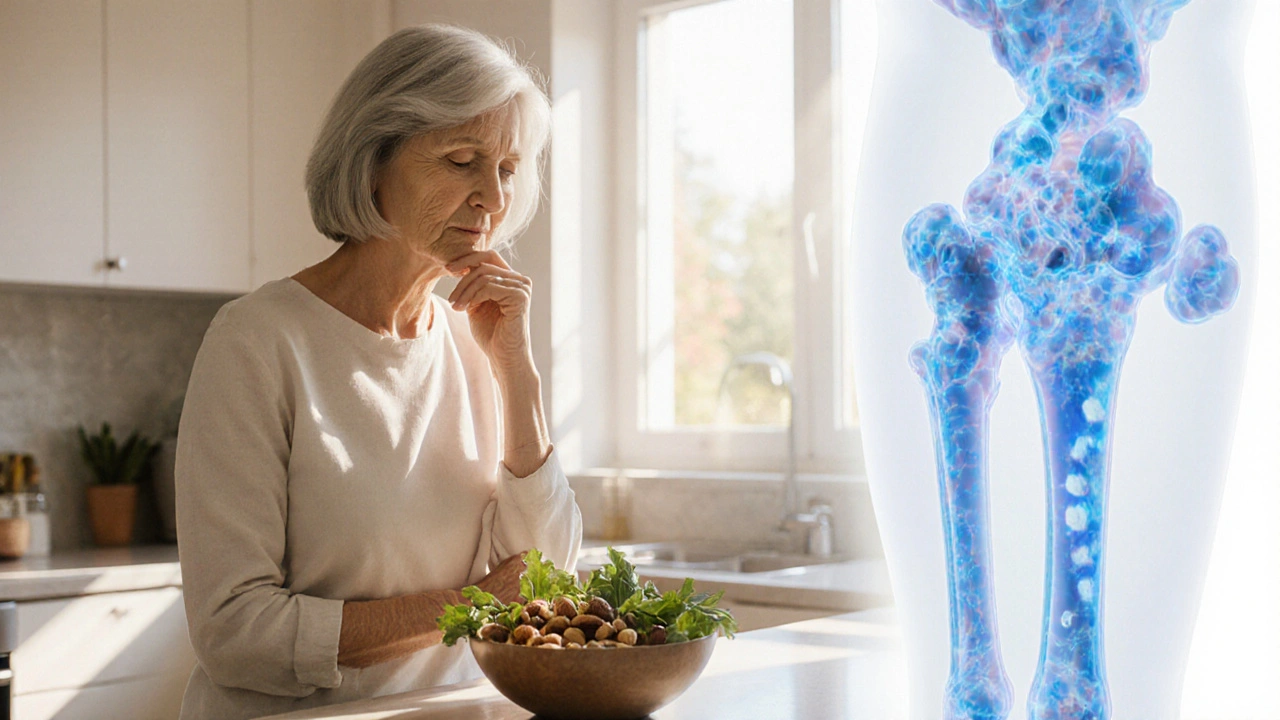
Menopause Bone Loss: Essential Facts for Women
Learn how menopause affects bone health, risk factors, nutrition, exercise, and treatment options to prevent osteoporosis and maintain strong bones.