UTI Treatment: What Works, What Doesn’t, and What You Need to Know
When you have a urinary tract infection, a common bacterial infection affecting the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. Also known as UTI, it’s one of the most frequent reasons people visit doctors—especially women. It’s not just discomfort; untreated UTIs can lead to serious kidney infections. The good news? Most UTIs respond quickly to the right treatment. But not all remedies work the same, and not every symptom needs antibiotics.
Antibiotics are the UTI treatment gold standard for bacterial infections, but which ones? Nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and fosfomycin are the top choices, based on current guidelines. They work fast—often easing symptoms in 24 to 48 hours. But overuse is a real problem. If you get UTIs often, your doctor might test for antibiotic resistance before prescribing. And no, drinking cranberry juice alone won’t cure an active infection, though some studies show it might help reduce recurrence by stopping bacteria from sticking to the bladder wall.
Recurrent urinary tract infection, when someone has three or more infections in a year. Also known as recurrent UTI, it’s not just bad luck—it’s often tied to anatomy, hormones, or even how you empty your bladder. Post-menopausal women, for example, may need vaginal estrogen to restore protective lining. And if you’re prone to UTIs after sex, a single antibiotic dose right after intercourse can cut risk by half. Don’t ignore symptoms like burning, frequent urges, or cloudy urine. Delaying treatment can turn a simple bladder infection into a kidney infection, which means hospital visits and stronger meds.
There’s a lot of noise out there about natural fixes—d-mannose, probiotics, garlic, apple cider vinegar. Some show promise in small studies, especially d-mannose, which may help flush out E. coli. But none replace antibiotics when you’re actively infected. And don’t skip the full course just because you feel better. Stopping early breeds resistant bacteria. The real win? Prevention: drink water, pee after sex, wipe front to back, and avoid irritating products like scented sprays or bubble baths.
What you’ll find below isn’t a list of miracle cures. It’s a collection of real, research-backed insights on how UTI treatment works in practice—from the antibiotics doctors actually prescribe, to the hidden triggers that cause repeat infections, to what happens when standard treatments fail. No hype. No guesswork. Just what you need to know to get better faster—and stay better.
- By Percival Harrington
- /
- 4 Dec 2025
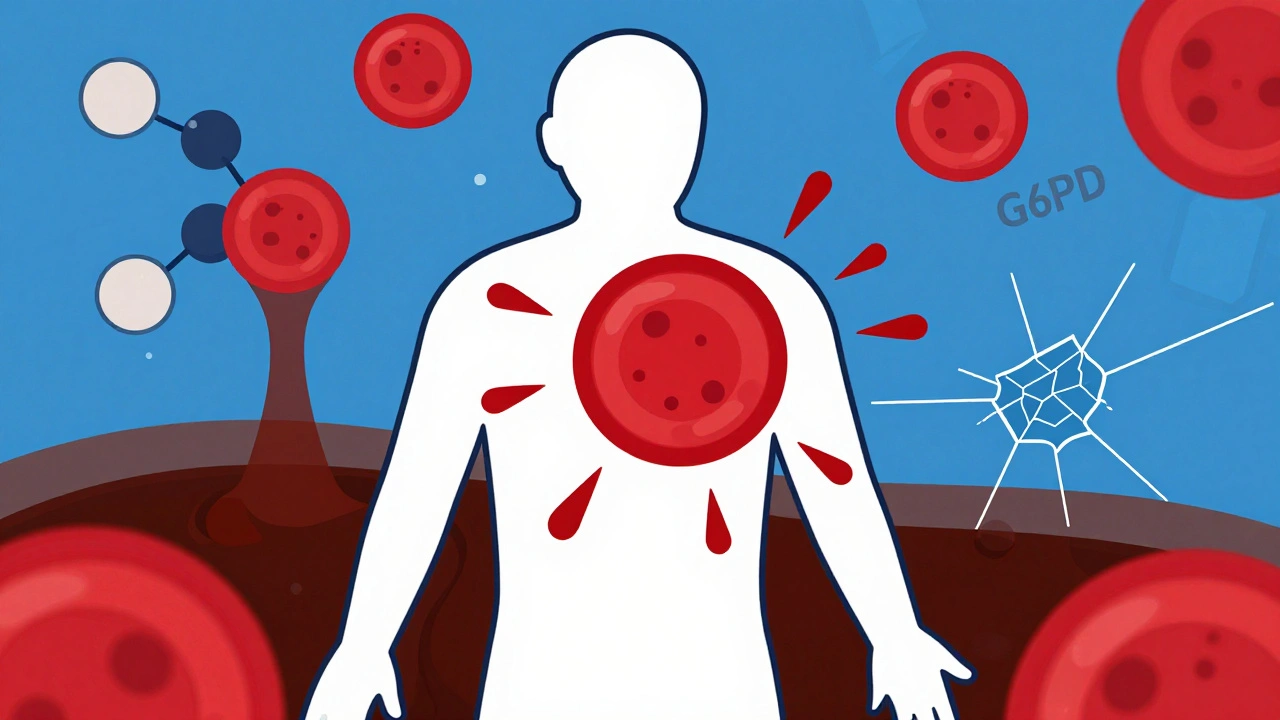
Nitrofurantoin and Hemolytic Anemia: What You Need to Know About G6PD Deficiency Risk
Nitrofurantoin can cause life-threatening hemolytic anemia in people with G6PD deficiency. Learn who’s at risk, what symptoms to watch for, and safer alternatives for treating UTIs.